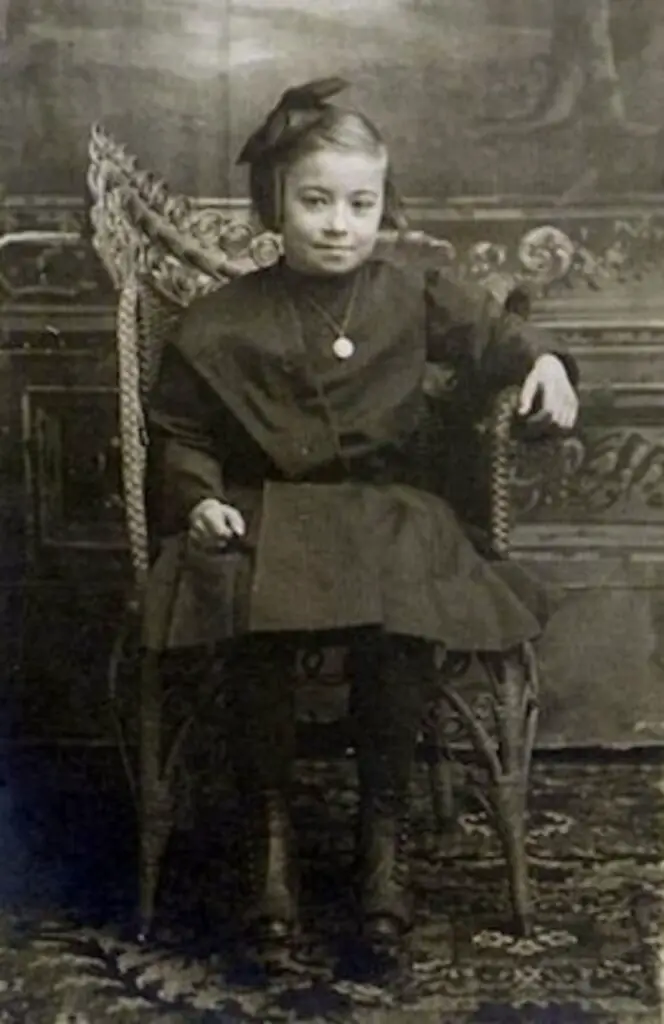
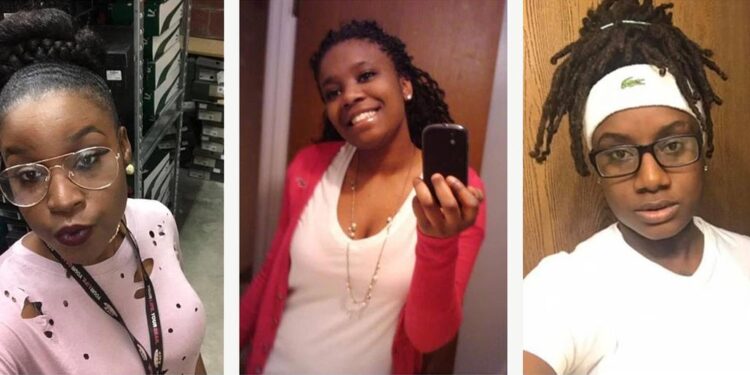In March 2018, a heartbroken mother named Donnita Stunson mailed a letter to the mayor of St. Louis asking for help. “I was born and raised in the city of St. Louis,” she wrote. “I was once proud of my city, until December 22, 2017.”
On that date, at around 3 a.m., an unknown number of people armed with guns broke into the apartment that Stunson’s daughter Dominique Lewis had recently moved into. Lewis and two of her friends ran outside — still in the clothes they wore to bed — frantically looking for somewhere to hide, and jumped into the back seat of one of their cars. The shooters found them and repeatedly fired into the vehicle, killing all three women. Police found their bodies huddled together in the car. “Looked like they were laying on top of each other,” one officer observed at the time.
Three months after the killings, Stunson decided to write her letter to then-Mayor Lyda Krewson. She was desperate for updates on the investigation, but detectives weren’t returning her calls. “As a mother, I am crushed, but I am disappointed too. I feel that there is no urgency in catching the murderers of these three young ladies,” Stunson wrote. “I am contacting you because I don’t know what else to do.”
The triple homicide was a shocking crime, even in one of the most violent cities in America. Lewis and her friends, Reeba Moore and Chanice White, were in their mid-20s. They worked, went to school and loved to socialize in the community. Police said they appeared to have been targeted for unknown reasons (none of the women had a criminal record). When Stunson walked through the apartment the morning after the shootings, she noticed that nothing seemed to have been stolen.

But for all the ways the killings of these young women stood out, the lack of progress on the case in the months and years that followed was, by contrast, quite typical. Of the roughly 1,900 homicides committed in the city of St. Louis from 2014 through 2023, more than 1,000 remain unsolved, according to an analysis of homicide data obtained by APM Reports and St. Louis Public Radio.
During those years, murders in St. Louis surged, making the city one of the nation’s deadliest. For most of the decade, police struggled to bring perpetrators to justice. A review of 20 years of data and records reveals some of the reasons why police failed to solve so many homicides, including shoddy detective work, lack of resources and an erosion of community trust.
In 2022 and 2023, St. Louis homicide detectives solved substantially more cases. Homicides went down, and the department solved 56% of the murders committed those years, their highest rate since 2013, according to the analysis.
Yet with each unsolved murder, grief ripples across the city, leaving families and friends yearning for closure and justice. It’s a pain that the Black community in St. Louis endures disproportionately. Black people, who are about 44% of the city’s population, made up around 90% of those killed between 2014 and 2023. Police solved fewer than half of the killings involving Black victims. By contrast, police cleared nearly two-thirds of cases involving White victims.
The city’s homicides, especially those that remain unsolved, tend to happen in geographic clusters, the data shows. In the Fairground neighborhood on the city’s north side, where Lewis, Moore and White were slain, the concentration of deadly shootings is staggering. There were at least 37 homicides in the area in the past decade, and nearly 60% remain unsolved. In high-crime neighborhoods like this one, talking to police can be dangerous.
This is 4240 John Ave. in St. Louis, where three young Black women were killed on December 22, 2017.
Steps away, a 17-year-old boy named Jared Elam was shot to death on Sept. 4th, 2014. He died just two days before his 18th birthday and a week before he was supposed to start college.
About a tenth of a mile away, on July 9, 2022, police found 38-year-old Montez Haines dead on the side of the road with several gunshot wounds.
Kamorra Sneed was 41 when she was shot and killed on April 24, 2018. She was the mother of five children and had just graduated from college.
Donald Belford was 43 when police found him shot to death on the balcony of a hotel on May 3, 2022.
Joel Boyd, a 41-year-old father and lifelong resident of St. Louis, died from multiple gunshot wounds on May 1, 2021.
In total, there are 40 unsolved homicides from the last decade within a half mile radius of 4240 John Ave.
After the triple homicide, police appealed to the public for tips. The families went public, holding vigils and begging for someone to come forward with information. Over the years, the nonprofit CrimeStoppers repeatedly offered reward money, but police never arrested any suspects.
Stunson said the mayor’s office never responded to her letter, though not long after she sent it, she received a rare phone call from a detective about her daughter’s murder. He had little progress to report.


St. Louis Metropolitan Police Department officials declined to be interviewed about the case, but a spokesperson wrote in an email that detectives are still actively investigating it. Police have said in the past that a lack of information from the public is their main obstacle. “Staffing and funding isn’t the problem in this case, clues are the problem,” Lt. John Blaskiewicz said in a 2022 interview with KMOV, a local television station.
Some experts believe that failing to solve homicides can lead to more violence. “If you’re not closing cases, then people are afraid,” said Dan Isom, a former St. Louis police commissioner who served as the city’s public safety director from 2021 to 2023. “There is a lot of correlation, if not causation, between confidence in the police and community violence,” Isom said. Without an arrest, some people might seek justice on their own.
Lewis was very close to her brother and sisters, so Stunson asked them to choose everything for the funeral. They picked a casket that was purple, her favorite color, and covered her vault in sparkles. They brought a scarf to the wake to cover the bullet wounds on her neck.


On Feb. 10, 2018, friends and family of the victims gathered for a candlelight vigil to pray and ask the public to come forward with information.
The night Lewis was killed, her younger sister, Danyelle Lewis, was supposed to have slept over at her apartment. Danyelle was gripped with anger about the killings and losing hope that police would catch the people who committed them. Stunson said Danyelle believed that some people attending the vigil knew something they weren’t telling the cops.
After the vigil, Danyelle got in her car and followed the group of people as their car merged onto a highway, according to police records. She had a gun. Danyelle pulled up beside the car and opened fire.
Lewis, Moore and White were among the final victims in 2017. It was one of the deadliest years in St. Louis, with a total of 207 people killed, according to the data.
As the number of cases surged, the percentage that police managed to “clear,” or resolve, was dropping. In 2019, data shows, police solved the lowest percentage of murders in at least 20 years, with nearly 70% unsolved. Nationwide, police clear about half of all homicides, according to The Washington Post.
Police cleared a higher percentage of cases in 2022 and 2023. And last year, the number of homicides dropped in St. Louis, as it has in cities across the country. Fewer killings means more resources can be devoted to each case. The department is also under new leadership — Robert Tracy was named chief in late 2022 — and police officials have said the improvement can be attributed, at least in part, to better surveillance coverage throughout St. Louis and stronger communication within the department.
Tensions between police and the community are longstanding in St. Louis. Those tensions worsened after a Ferguson, Missouri, officer killed 18-year-old Michael Brown in 2014, said Jay Schroeder, president of the St. Louis Police Officers Association. “I think a lot of the mistrust of the police started to grow.”
The department’s detectives were under enormous pressure, Schroeder said, especially in 2020, when the number of murders in St. Louis hit a near record of 263.
While the number of killings was rising, St. Louis officials reduced the homicide unit’s budget and supplemented it with increased spending on overtime. The city spent about $18,000 for each homicide investigation in fiscal year 2012. By fiscal year 2020, it was less than $12,000. It has since rebounded to about $15,000 per investigation in 2022.
The city has also failed to invest in crime-fighting tools, and still has a DNA-evidence backlog of hundreds of samples from homicides. That forces detectives to wait for key evidence in their cases.
Still, some detectives have failed to do basic investigative work.
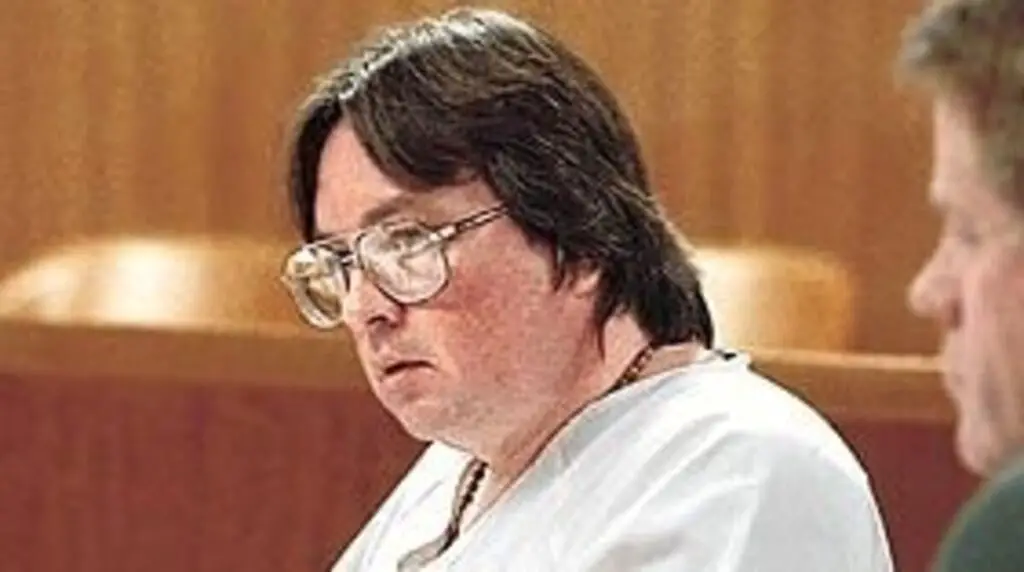
The officer assigned to the killings of Lewis, Moore and White was Det. Craig Robertson. At a vigil held shortly after the killings, Robertson told the crowd about his commitment to the case. “This one’s bothered me the most,” he said. “I’m not going to stop. We’ll figure it out.”
But the victims’ families say his public statements didn’t align with his actions. His supervisor, Sgt. Heather Taylor, wrote in 2019 that Robertson “failed to complete basic investigative follow-ups” in his cases, including in one instance, not checking suspects’ phone location data and vehicle registration, according to memos obtained by St. Louis Public Radio and APM Reports. Taylor also wrote that Robertson did not stay in contact with murder victims’ families. Many families interviewed for this series said their calls to other St. Louis homicide detectives were never returned.
Taylor wrote in her memo that she intended to continue supervising Robertson’s investigation into the killings of Lewis, Moore and White. She noted that he cleared 14% of the cases assigned to him in 2018, the lowest rate, by far, of any detective under her supervision. Robertson declined to comment.
The 2017 triple homicide was still assigned to Robertson in early 2024, a spokesperson said. But in May, he decided to retire from the department. Stunson said she hasn’t talked to him in years. She has spent so long unsuccessfully calling him for updates, she can’t bear to try anymore.
Dominique Lewis was the type of person who took care of the people around her, Stunson said. She would clean her grandma’s house and take her grandpa to his doctor’s appointments. She’d had the same group of girlfriends since elementary school. She loved reading and always had a book with her. She also had a ditzy side, Stunson said, which made everyone in the family laugh. Her dream was to one day be a school guidance counselor.
Lewis’ sister Danyelle was the one in the family who always tried to protect her other siblings, though she was the youngest of the bunch, Stunson said. The family called her “the enforcer.”
Luckily, the bullets Danyelle fired at the people in the car did not hit anyone. She was soon arrested, pleaded not guilty and was put in jail to await trial. After months of not hearing from homicide detectives about Dominique’s murder, Stunson said, she got a call from a police officer trying to build a case against Danyelle.
Stunson said she changed the subject to her murdered daughter. “How about looking into that?” she remembers telling the detective. She never heard from him again.
People who commit violent crimes have often suffered violence or trauma themselves, said Jessica Meyers, director of the St. Louis Area Violence Prevention Commission. “They may decide to take justice into their own hands,” she said. “The victim pool and the perpetrator pool kind of overlap, and the cycle just continues to perpetuate.”
Lisa LaGrone has worked in violence prevention in St. Louis for decades and says that one of the reasons so many homicides go unsolved is apathetic police officers who blame victims’ lifestyles for their deaths. She started her mission to reduce murders in the community after her father and little brother were shot and killed eight months apart in the early 1990s. Both homicides remain unsolved.

In the past few years, two of LaGrone’s grandsons were also killed, including Demetrion Simmons, who was fatally shot after witnessing the killing of his friend, 19-year-old Isis Mahr. Simmons identified the shooters to police and was the only witness willing to testify. LaGrone believes he was killed in retribution. After Simmons was killed, prosecutors dropped the charges against the two teenagers accused of killing Mahr.
LaGrone said police often point to a lack of community cooperation, but then overlook the reasons why residents hold back. “If your community knows they’re not gonna be protected, they’re not gonna step up,” LaGrone said. “But it’s still your job to police and be the detectives.”
Stunson says she still doesn’t know what happened the night her daughter was killed. A police minister privately informed her that someone inside the apartment called 911 to report a burglary in progress, she said, but she has never heard those recordings. Police refused to make the 911 audio public because the investigation is still open. The department did release a dispatch log that shows someone called the police around 3 a.m.
Moore’s boyfriend was also in the apartment but escaped, according to police records.
In 2019, Danyelle Lewis pleaded guilty to several charges, including assault. The judge sentenced her to six years in prison, and she was released in 2023. She declined an interview request for this story.
Stunson says that while Danyelle’s struggles with grief and anger led her to prison, many in her family have turned to alcohol to cope with Dominique’s murder. Stunson prays that whoever knows something will “get a conscience” and give information to the police so that everyone can find the closure they are so desperately seeking.
“When something like this happens, people don’t realize, it’s not just the person that they murdered,” Stunson said. “It impacts the whole family.”
This article was published as a collaboration among St. Louis Public Radio, The Marshall Project and APM Reports, as part of the Public Media Accountability Initiative, which supports investigative reporting at local media outlets around the country.
Map sources: Aerial imagery from Missouri Spatial Data Information Service and National Agriculture Imagery Program. Neighborhood boundaries from City of St. Louis. Homicide data from 2004 through 2023, provided by the St. Louis Metropolitan Police Department and analyzed by APM Reports and The Marshall Project.